What Do Symbols On Iso Drawings Mean
A piping and instrumentation diagram (P&ID) is a detailed diagram in the process manufacture which shows the pipe and process equipment together with the instrumentation and control devices.
Superordinate to the P&ID is the procedure flow diagram (PFD) which indicates the more general catamenia of plant processes and the relationship between major equipment of a institute facility.
Contents and part [edit]

Example of a unmarried industrial control loop; showing continuously modulated control of process flow.
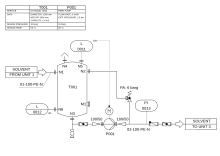
Piping and instrumentation diagram of pump with storage tank. Symbols co-ordinate to EN ISO 10628 and EN 62424.

A more complex example of a P&ID.
A pipe and instrumentation diagram (P&ID) is defined as follows:
- A diagram which shows the interconnection of process equipment and the instrumentation used to control the process. In the process industry, a standard set of symbols is used to prepare drawings of processes. The musical instrument symbols used in these drawings are mostly based on International Society of Automation (ISA) Standard S5.ane
- The primary schematic drawing used for laying out a process control installation.
They normally contain the following data:
- Mechanical equipment, including:
- Pressure vessels, columns, tanks, pumps, compressors, heat exchangers, furnaces, wellheads, fans, cooling towers, turbo-expanders, pig traps (see 'symbols' below)
- Bursting discs, brake orifices, strainers and filters, steam traps, wet traps, sight-glasses, silencers, flares and vents, flame arrestors, vortex breakers, eductors
- Procedure piping, sizes and identification, including:
- Pipe classes and pipage line numbers
- Flow directions
- Interconnections references
- Permanent get-go-upward, flush and featherbed lines
- Pipelines and flowlines
- Blinds and spectacle blinds
- Insulation and estrus tracing
- Process control instrumentation and designation (names, numbers, unique tag identifiers), including:
- Valves and their types and identifications (e.g. isolation, shutoff, relief and safety valves, valve interlocks)
- Control inputs and outputs (sensors and concluding elements, interlocks)
- Miscellaneous - vents, drains, flanges, special fittings, sampling lines, reducers and swages
- Interfaces for grade changes
- Computer control organisation
- Identification of components and subsystems delivered by others
P&IDs are originally drawn up at the pattern stage from a combination of process flow sheet data, the mechanical procedure equipment design, and the instrumentation engineering design. During the blueprint phase, the diagram too provides the basis for the development of system command schemes, allowing for further safety and operational investigations, such equally a Run a risk and operability study (HAZOP). To practice this, information technology is disquisitional to demonstrate the physical sequence of equipment and systems, too as how these systems connect.
P&IDs also play a meaning part in the maintenance and modification of the process afterwards initial build. Modifications are red-penned onto the diagrams and are vital records of the current plant design.
They are also vital in enabling development of;
- Control and shutdown schemes
- Condom and regulatory requirements
- Start-up sequences
- Operational understanding.
P&IDs grade the basis for the live mimic diagrams displayed on graphical user interfaces of big industrial control systems such every bit SCADA and distributed control systems.
Identification and reference designation [edit]
Based on STANDARD ANSI/ISA S5.i and ISO 14617-6, the P&ID is used for the identification of measurements within the process. The identifications consist of upward to 5 letters. The start identification letter is for the measured value, the 2d is a modifier, 3rd indicates passive/readout function, 4th - active/output function, and the 5th is the function modifier. This is followed past loop number, which is unique to that loop. For example FIC045 means information technology is the Flow Indicating Controller in control loop 045. This is too known as the "tag" identifier of the field device, which is normally given to the location and part of the instrument. The same loop may have FT045 - which is the menstruation transmitter in the same loop.
| Letter of the alphabet | Column 1 (Measured value) | Column 2 (Modifier) | Column 3 (Readout/passive office) | Column 4 (Output/agile function) | Column 5 (Function modifier) |
| A | Analysis | Alarm | |||
| B | Burner, combustion | User selection | User choice | User choice | |
| C | User'southward selection (usually conductivity) | Control | Close | ||
| D | User'south choice (usually density) | Deviation | Deviation | ||
| E | Voltage | Sensor | |||
| F | Flow rate | Ratio | |||
| G | User'southward choice (usually gaging/gauging) | Gas | Glass/gauge/viewing | ||
| H | Hand | High | |||
| I | Electric current | Indicate | |||
| J | Ability | Scan | |||
| K | Time, time schedule | Time charge per unit of change | Command station | ||
| L | Level | Light | Low | ||
| Grand | User'due south choice | Eye / intermediate | |||
| N | User's choice (unremarkably torque) | User choice | User choice | User choice | |
| O | User'due south choice | Orifice | Open | ||
| P | Pressure | Point/test connexion | |||
| Q | Quantity | Totalize/integrate | Totalize/integrate | ||
| R | Radiation | Tape | Run | ||
| Southward | Speed, frequency | Safety (Non Sister (S5.1)) | Switch | Finish | |
| T | Temperature | Transmit | |||
| U | Multivariable | Multifunction | Multifunction | ||
| 5 | Vibration, mechanical analysis | Valve or damper | |||
| W | Weight, force | Well or probe | |||
| X | User's choice (usually on-off valve as XV) | 10-axis | Accessory devices, unclassified | Unclassified | Unclassified |
| Y | Issue, state, presence | Y-axis | Auxiliary devices | ||
| Z | Position, dimension | Z-axis or Safety Instrumented System | Actuator, driver or unclassified final command element |
For reference designation of any equipment in industrial systems the standard IEC 61346 (Industrial systems, installations and equipment and industrial products — Structuring principles and reference designations) tin can be applied. For the function Measurement the reference designator B is used, followed by the to a higher place listed letter of the alphabet for the measured variable.
For reference designation of any equipment in a power station the KKS Ability Plant Classification Organization tin be applied.
Symbols of chemic apparatus and equipment [edit]
Below are listed some symbols of chemical apparatus and equipment unremarkably used in a P&ID, according to ISO 10628 and ISO 14617.
| | Pipe | | Thermally insulated pipe | | Jacketed piping | | Cooled or heated piping |
| | Flexible connection | | Hydraulic pump | | Pump | | Vacuum pump or compressor |
| | Fan | | Centric fan | | Radial fan | | Dryer |
| | Jacketed mixing vessel (autoclave) | | Half pipe mixing vessel | | Pressurized horizontal vessel | | Pressurized vertical vessel |
| | Packed cavalcade | | Plate column | | Furnace | | Cooling belfry |
| | Heat exchanger | | Curlicue heat exchanger | | Cooler | | Plate & frame heat exchanger |
| | Double pipe heat exchanger | | Stock-still straight tubes oestrus exchanger | | U shaped tubes heat exchanger | | Spiral heat exchanger |
| | Covered gas vent | | Curved gas vent | | Air filter | | Funnel or tundish |
| | Steam trap | | Viewing glass | | Pressure reducing valve | | Valve |
| | Gate valve | | Control valve | | Transmission valve | | Check valve |
| | Needle valve | | Butterfly valve | | Diaphragm valve | | Brawl valve |
| | Check valve | | Back draft damper | | Handbag | | Gas canteen |
 | Earth valve |  | 3-way valve |  | Piston or reciprocating compressor |  | Relief valve |
| Rupture disc | Turboexpander | Centrifugal pump | Reciprocating pump |
Historical use [edit]
Prior to the appearance of Computer Aided Blueprint (CAD) in the late 1980s, P&IDs were drawn past hand. The drawing template shown below, actual size 225 mm by 111 mm, is typical of those used to draw P&IDs.

Piping and Instrumentation Diagram manual drawing template (1980s)
Symbol Primal:
A – Vessel dished end
B – Motor driven pump or compressor and baseplate
C – Valves
D – Valve diaphragm actuator
E – Vanquish and tube oestrus exchanger
F – Flexible hose, bellows
G – Ejector
H – Car driven pump or other device
I – Reducers
Meet also [edit]
- Instrumentation in petrochemical industries
External links [edit]
- Commons:Category:Chemical engineering science symbols - A list of P&ID symbols in SVG format
- Larn How to Read P&ID Drawings – A Complete Guide
- Interpreting Pipage and Instrumentation Diagrams-Symbology
- How to Node P&IDs for a HAZOP - Learn how to Node P&IDs for a HAZOP
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Piping_and_instrumentation_diagram
Posted by: listergioncy.blogspot.com












































0 Response to "What Do Symbols On Iso Drawings Mean"
Post a Comment